A Mill Certification Report is a certified record of the physical and chemical properties of raw materials and is used in the metal industry—more specifically, for steel, stainless steel, and alloy materials. This quality assurance document certifies that the metal has been produced to meet the minimum requirements set by manufacturing standards, such as ANSI, ASME, ASTM, AWWA, or others.
An MTR (Material Test Results) report is a record used by manufacturers and fabricators, including metal distributors, machine shops, manufacturers of piping system components, for automotive use, and other metal suppliers. The information in this report is derived from the information found on the Mill Certification Report, and it is the report that we provide to our customers.
Reviewing Mill Certs and MTRs is an essential piece of the quality control process. The reports are analyzed to ensure the material quality of all our metallic parts—including all stocked or manufactured flange options, fittings, accessories, or any other custom parts produced in our machine shop—meets the specific material specification. No matter the product, examining the raw materials against the Mill Cert is an important step in the manufacturing and production of metal products and parts for piping systems.
What Is Included in Mill Certs or MTRs?
Mill Certs and MTRs are standard documents used by manufacturers to show information about either the raw material or finished product. The reports show full physical and chemical results referenced typically by the size of the raw material or by the part number for specific heat (batch) numbers. While the report format may vary from mill to mill (for Mill Certs) or manufacturer/fabricator (MTRs for their finished product), the required information in the report is the same.
| Item | Mill Certification | Materials Test Report (MTR) |
|---|---|---|
| The part number for the finished product | X | X |
| The measurements of the product, including thickness and weight | X | |
| The mechanical properties of the material | X | X |
| The specific chemical properties of the material | X | X |
| The spec number and/or material grade | X | X |
| Any special requirements or features of the material beyond the standards | X | |
| All methods used in milling the product | X | |
| Any special requirements or features of the material, beyond the standards | X | |
| The signature of the certifying mill employee | X | |
| A stamp of approval or signature of the employee approving the material | X |
Some standards require confirmation by an agent from an independent inspection agency. If this is the case, Mill Certs or MTRs may display a second certifying signature.
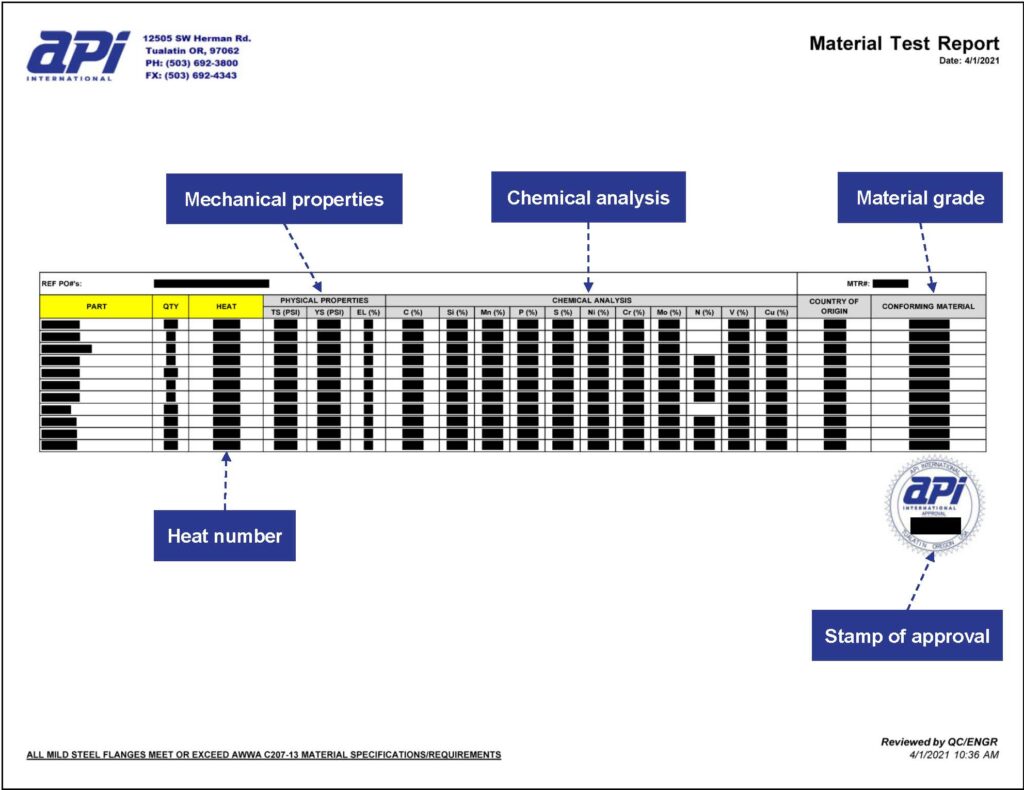
How to Read API International Materials Test Results (MTR)
When determining the best quality raw materials for sourcing piping system components, including fittings, flanges, and valves—and for other industries and metalworking needs—the first step is to consult the MTR. The Mill Certification is not provided to buyers, however, any relevant information regarding required items, analysis, and properties are provided in the API International MTR.

The heat number or batch number, also called a heat code lot number, is used to trace the material’s origin to ensure metal quality. It’s similar to a batch number as it relates to quality control in manufacturing facilities. This number should match the number that is printed or stamped on the surface of the material. The manufacturer will compare the heat number on the Mill Cert to the code (or reference number) on the raw material when selecting or receiving the material.
The material grade indicates the results of the mechanical and chemical composition analysis and states the properties of the metal. This section discloses the percentage values of chemical proportions and will meet the requirements specified by agencies, such as American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) or American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) standards. This is displayed on the MTR as A- for ASTM or SA for ASME.
Mechanical properties are used to determine if the material meets the specifications for an intended application. Tensile and yield stress testing, elongation at break, and other mechanical tests are conducted to determine the raw material’s thresholds, including how well the metal will tolerate welding.
Chemical analysis of the material is another way to certify that the material can withstand intended applications. In order to use the raw material in manufacturing, the material chemical composition must be within the range included in the specific set of standards.
Additional specifications are listed as well, if necessary. If your order requires any further tests or certifications, they will be noted within the MTR. This section may include information regarding the finishes or other details.
A stamp of approval and/or signature is included, and this signature is provided by a qualified employee that has reviewed the Mill Cert and the accompanied MTR to attest to the accuracy of the report. If the standards require an independent contractor to certify the report, that information will also be included near the employee’s signature.
The MTR is an important method of approving material for manufacturers in the metals industry because it provides the necessary information to ensure the raw material meets the requirements for the production of metal goods, including flanges and piping system components. The report is also a record of the material’s origin, which ensures quality. These reports are used while raw materials are inspected, then retained by the manufacturer.
An MTR is also an important document for determining if the raw material is suitable for the desired application, whether the material is used for flanges or for custom machining. This report is specific to manufacturers and distributors of steel and alloy products and can be used to verify the quality of the finished product. Contact us with questions, special requests, or to ensure products meet your project’s specifications.